Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare but serious autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves. This can lead to muscle weakness, numbness, and, in severe cases, paralysis. While GBS can affect individuals of all ages, it is more prevalent in adults and males.
What causes GBS?
The exact cause of GBS remains unclear; however, it often follows an infection. In around two-thirds of cases, indications occur days or weeks after a respiratory or gastrointestinal contamination. One of the most common bacterial triggers is Campylobacter jejuni, frequently found in undercooked poultry. Other associated infections include:
- Influenza virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Zika virus
- Hepatitis A, B, C, and E
- HIV
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
In rare instances, GBS has been linked to recent surgeries or vaccinations. Notably, during the 1976 swine flu vaccination campaign, there was a slight increase in GBS cases, leading to ongoing vaccine safety monitoring. Recent studies have found a very low risk of GBS following vaccinations, including those for influenza and COVID-19. For example, the U.S. FDA has required GSK and Pfizer to include warnings about a potential increased risk of GBS with their RSV vaccines, though the evidence is inconclusive.
Symptoms of GBS

GBS symptoms can progress rapidly, often over several days to weeks. Common signs include:
- Weakness or tingling sensations, starting in the legs and potentially spreading to the arms and face
- Difficulty with eye muscles and vision
- Problems swallowing, speaking, or chewing
- Severe pain, particularly at night
- Coordination problems and unsteadiness
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Blood pressure fluctuations
- Digestive and bladder issues
In severe cases, muscle weakness can escalate to paralysis, affecting respiratory muscles and necessitating ventilatory support. Prompt medical attention is crucial to manage and mitigate the progression of symptoms.
How to avoid GBS?
While it is not possible to prevent GBS entirely, certain measures can decrease the risk:
- Proper food handling: Since Campylobacter jejuni is a known trigger, ensure all poultry is cooked thoroughly. Avoid consuming undercooked or raw chicken.
- Hygiene Practises: Regular handwashing can prevent infections that might trigger GBS.
- Vaccinations: Stay updated with recommended vaccinations, as preventing infections like influenza can reduce the risk of subsequent GBS.
- Prompt medical care: Seek immediate medical attention for infections to reduce complications.
Treatment and recovery
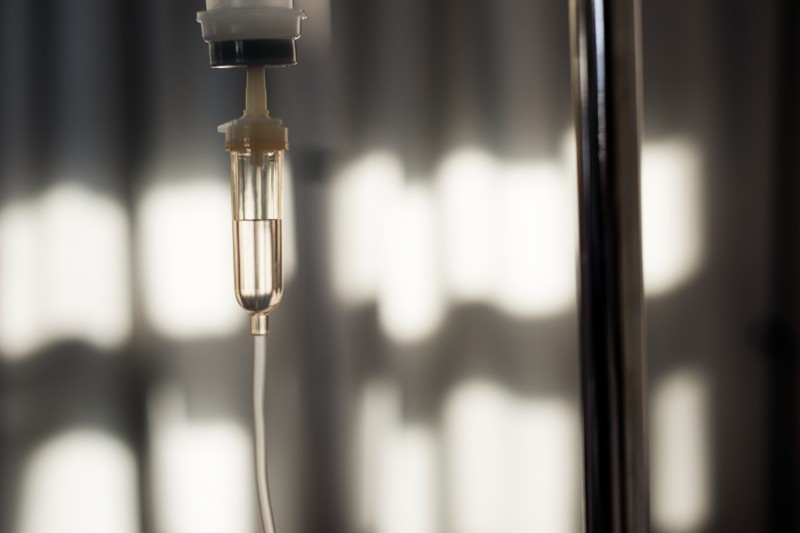
There is no known cure for GBS; however, treatments can alleviate symptoms and expedite recovery. Common interventions include:
- Plasma exchange (Plasmapheresis): This process removes antibodies from the blood attacking the nerves.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): Administering immunoglobulins can block the harmful antibodies.
- Supportive care: Monitoring respiratory function, heart rate, and blood pressure is essential. In cases where breathing is compromised, mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy can aid in regaining strength and mobility during recovery.
Most individuals with GBS experience a full recovery, though some may have lingering effects like weakness or numbness. Early diagnosis and treatment are pivotal in improving outcomes.
In summary, Guillain-Barré Syndrome is a rare neurological disorder often triggered by infections. Awareness of its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures can aid in early recognition and management, enhancing the likelihood of a full recovery.
If you encounter sudden muscle shortcomings or other neurological indications, look for restorative consideration immediately.
Key Takeaways
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves.
- A respiratory or gastrointestinal infection, influenza, Zika virus, and HIV can lead to GBS.
- Symptoms of GBS include weakness, difficulties in swallowing, intense pain, and irregular heart rhythms.
- Proper food handling, hygiene practices, and vaccinations can reduce the risk.
- Treatments include plasma exchange, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and supportive care.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Keep up to date with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruat ABHI karo.
You may also be interested in the following blogs:
- 5 Key Causes Of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome You Need To Know
- Exploring The 3 Types Of Down Syndrome: What You Need To Know
Popular Searches
How to lower blood pressure | Fruits good for liver | Unhealthy foods | Ragi Benefits | Basal Metabolic Rate | Acupressure points for High Blood Pressure | Ayurvedic medicine for blood pressure | How to control cholesterol at home | Homeopathy for Asthma | Biological Age | Home remedies for TB | Natural beta blockers | Negative effects of internet | Types of walking | Blood pressure calculator | Blood sugar calculator | BMI Calculator





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000