Kidney stones are solid clusters of minerals and salts that form in the urine. While they can sometimes pass naturally through the urinary tract, the process can be extremely painful.
What are kidney stones?
Urine contains wastes dissolved in it. Crystals form when a lot of waste is present in a little liquid. They attract other elements and combine to create a solid that will consolidate unless passed out of the body with the urine. The kidneys usually eliminate these chemicals in the urine.
However, if they are formed, the stones may stay in the kidney or pass into the ureter. Tiny stones move out of the body in the urine, sometimes without causing much pain. However, stones that stay in the kidney, ureter, bladder, or urethra may cause pain.
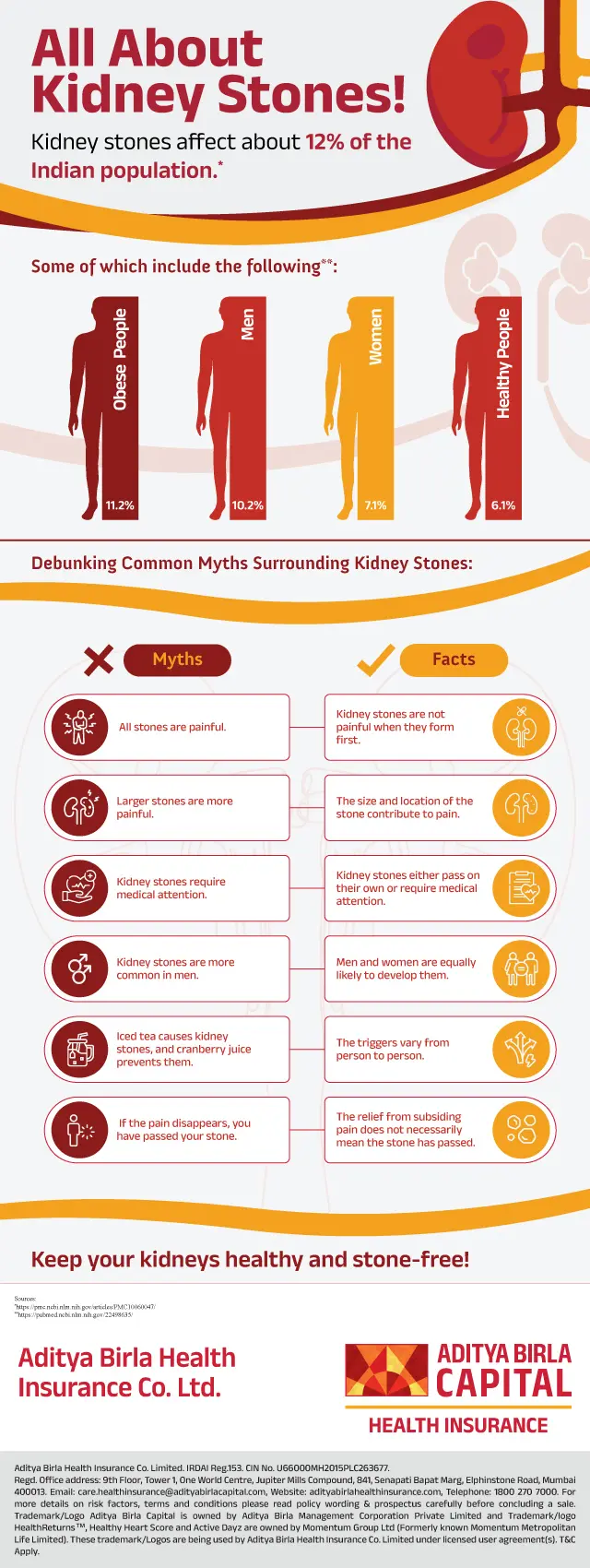
How common are kidney stones?
Approximately one in ten people will experience a kidney stone at some point in their lifetime. They are most common in people assigned male at birth (AMAB) in their 30s and 40s. They are also more common among non-Hispanic white people.
3 Symptoms of kidney stones
Kidney stones can vary in size, ranging from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a pebble, with some even reaching the size of a golf ball. In general, the larger the stone, the more pronounced the kidney stone symptoms, which may include one or more of the following:
Severe and intermittent pain
If a kidney stone gets stuck in the ureters, it can obstruct urine flow, leading to kidney swelling and ureter spasms (called renal colic), which can be extremely painful. At that point, you may experience:
- Intense, sharp pain in the side and lower back, just beneath the ribs
- Discomfort that extends to the lower abdomen and groin
- Pain that occurs in waves and varies in intensity
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating
Blood in the urine
Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Pink, red or brown urine
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
A small amount of blood in urine, called hematuria, can be detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the blood is visible as spots in the water after urinating.
Frequent urination
You may also feel a persistent need to urinate frequently, even if you have just finished. However, you may pass only a small amount of urine.
Causes of kidney stones
The exact cause of kidney stones is unclear mainly, but some factors can increase the risk.
Dehydration

Dehydration commonly causes kidney stones. When you are dehydrated, urine becomes more concentrated, making it easier for minerals and salts to crystallize and form stones. Concentrated urine also contains more substances like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, which can precipitate crystals that form kidney stones.
Diet
Consuming some foods and beverages in excess can raise the risk of forming kidney stones:
- Oxalate: Beets, black pepper, black tea, chocolate, nuts, potatoes, soy products, and spinach
- Purine: Red meat, organ meats, beer, meat-based gravies, sardines, and shellfish
- Calcium: Coffee, tea, and soda
- Sodium: Canned, packaged, and fast foods, as well as condiments, seasonings, and meats
- Animal protein: Chicken, pork, fish, and eggs
Medical conditions
Certain medical conditions can lead to forming kidney stones, such as:
- Gout: A disorder that causes painful swelling in the joints.
- Hyperparathyroidism: A condition where the parathyroid glands release too much parathyroid hormone, which causes high levels of calcium in the blood.
- Hypercalcemia: A condition where the blood has too much calcium.
- Urinary tract infections: An infection in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Diagnosis and types of kidney stones
Kidney stone diagnosis starts with a medical history, physical examination, and tests. Doctors diagnose kidney stones using imaging techniques, along with blood and urine tests.
The four primary kidney stone types are:
- Calcium oxalate: It is the most common type of kidney stone, formed when calcium binds with oxalate present in urine. A lack of calcium, fluid intake, and other conditions may contribute to their formation.
- Uric acid: It is another frequently occuring kidney stone. Organ meats and shellfish contain high concentrations of a natural chemical compound called purines. A high intake of purine increases the production of monosodium urate, which can lead to kidney stone formation. These types of stones often run in families.
- Struvite: These are less common and often develop as a result of infections in the upper urinary tract.
- Cystine: These occur in individuals with a genetic condition called cystinuria, which causes the kidneys to excrete excessive amounts of a specific amino acid.
Treatment options
The treatment approach varies based on the type of kidney stone and the severity of your symptoms.
Pain management
Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine for some types of stones to prevent them from forming or help them pass through your urinary system.
Increased fluid intake
The treatment for kidney stones is generally the same for both children and adults. You may be asked to drink a lot of water, and doctors try to let the stone pass without surgery.
Medical procedures
Medical treatment options include the following:
- Lithotripsy removes stones in the kidney or ureter slightly smaller than half an inch (1.25 centimeters). It uses sound or shock waves to break the stones into tiny fragments, leaving the body in the urine.
- Ureteroscopy can be used to treat stones in the lower urinary tract, where a laser is applied to break the stone into smaller fragments.
- Surgery may be needed if other methods do not work or are not possible, in rare cases.
When should you see a doctor?

Make an appointment with your doctor for any signs and symptoms that worry you. If you have a kidney stone, you will need to know where it is located and what size it is so you can get treated and prevent complications. Seek urgent medical care if you experience:
- Severe pain that makes sitting still difficult
- Pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting
- Pain accompanied by fever and chills
- Blood in your urine
- Difficulty passing urine
Kidney stones can be daunting and painful. Consult your healthcare provider to prevent your situation from worsening. Do not skip your prescriptions, drink lots of water and follow dietary guidelines. Also, remember that kidney stones are temporary. Take good care of yourself to support overall health and keep this condition at bay.
Key Takeaways
- Kidney stones are hard, mineral-based deposits that form in the kidneys due to high levels of certain substances in the urine.
- The four main types of kidney stones are calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine.
- They can cause pain, blood in the urine, and frequent urination.
- Dehydration, a diet high in sodium and oxalate, and medical conditions like gout can cause them.
- Treatment options include taking medications, increasing your fluid intake and medical procedures.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Keep up to date with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruat ABHI karo.
You may also be interested in the following blogs:
Popular Searches
How to lower blood pressure | Fruits good for liver | Unhealthy foods | Ragi Benefits | Basal Metabolic Rate | Acupressure points for High Blood Pressure | Ayurvedic medicine for blood pressure | How to control cholesterol at home | Homeopathy for Asthma | Biological Age | Home remedies for TB | Natural beta blockers | Negative effects of internet | Types of walking | Blood pressure calculator | Blood sugar calculator | BMI Calculator





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000







