Muscles are essential for the proper functioning of the human body. They are necessary for movement, support, and many other functions. Without them, walking, lifting objects, the rise and fall of the chest, and the most basic function keeping you alive – breathing is impossible. Muscle loss is usually caused by not exercising your muscles regularly. Your inability to move may be due to an underlying health condition or injury.
What is muscle loss (Sarcopenia)?
Sarcopenia is progressive muscle mass and strength loss with age. It is a type of muscle atrophy primarily caused by natural aging. Inactivity and an unhealthy diet can lead to the disease. Sarcopenia can significantly impact one’s quality of life by reducing one’s ability to perform daily tasks, leading to a loss of independence and the need for long-term care. It adversely impacts one’s musculoskeletal system and increases weakness, fractures, and falls. This can lead to hospitalizations and surgeries, which increase the risk of complications.
The impact of muscle loss on overall health
A decrease in the number and size of your muscle fibers causes your muscles to be thin (muscle atrophy). As you age, your body undergoes specific changes that majorly factor in developing sarcopenia. For instance, your body does not produce the same quantity of proteins your muscles need to grow. With this, your muscle cells get smaller.
Causes of muscle loss
Muscle loss can occur for a number of reasons. Let us look at the following muscle loss causes:
Aging
Our bodies produce fewer proteins that promote muscle growth as we age. This causes the muscle cells to shrink, resulting in sarcopenia. According to a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) report, sarcopenia impacts up to a third of people of ages 60 and above. Other than reduced muscle mass, sarcopenia can cause:
- Weakness or frailty
- Poor balance
- Difficulty moving
- Lower endurance
Inactivity
A lack of physical activity for a prolonged period can also cause muscle loss. If a muscle is unused, the body eventually breaks it down to preserve energy. Muscle atrophy developing due to inactivity can happen if a person remains immobile while recovering from an illness or injury. Regular exercise and physical therapy may reverse this form of muscle atrophy.
Hormonal changes
Here are the key points regarding hormonal changes and muscle loss:
- Declining testosterone levels with age contribute to muscle loss in men.
- A drop in IGF-1 (Insulin-like growth factor 1, a hormone that helps with growth, development, and metabolism) levels significantly impacts muscle mass.
- During menopause, the decline in estrogen can lead to muscle loss in women as estrogen has a protective effect on muscle tissue.
- High cortisol (stress hormone) levels can promote muscle breakdown and contribute to muscle loss.
Chronic diseases
The following chronic diseases can contribute to muscle atrophy:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurological disease that destroys the motor nerve cells controlling the muscles.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic condition in which your immune system attacks the nervous system, causing inflammation in the nerve fibers.
- Arthritis is inflammation of the joints, causing pain and stiffness. It can severely limit mobility and lead to muscle disuse and atrophy.
- Myositis refers to inflammation of the muscles, causing muscle weakness and pain.
- Polio is an infectious disease attacking the nervous system and causing flu-like symptoms, which can result in permanent paralysis.
- Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts.
- Kidney failure is when your kidneys stop working well.
Medications
Many medications, including statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs), corticosteroids (used to treat arthritis, asthma, and COPD), antiarrhythmics (used to treat heart rhythm problems), and some others, can cause muscle loss. This condition is called drug-induced myopathy or muscle injury.
Malnutrition
Poor nutrition and diets low in lean protein can reduce muscle mass, causing atrophy. It develops as a result of medical conditions that disrupt the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, such as:
- Irritable bowel syndrome: A condition that affects the function of the digestive tract
- Celiac disease: An autoimmune disorder in which the immune system responds negatively to gluten
- Cancer: A disease that results when cellular changes cause cells to grow and divide uncontrollably
Recognizing the symptoms of muscle loss
Muscle loss symptoms differ extensively based on the cause and severity of muscle loss.
Decreased strength and power

A key symptom of muscle loss is a noticeable decrease in strength and power, called muscle weakness.
Difficulty with daily activities
Due to reduced strength and endurance, you may find performing the following everyday activities challenging:
- Walking
- Climbing stairs
- Getting up from a chair
- Carrying groceries
- Reaching overhead
- Getting out of a car
- Opening jars
Increased fatigue and weakness
When muscle mass decreases, the body’s ability to generate power and perform activities is reduced, resulting in tiredness and weakness.
Changes in gait and balance
A significant symptom of muscle loss is noticeable changes in gait (walking pattern) and balance, often due to decreased muscle strength in the legs and core. This makes it harder to maintain stability while walking or standing.
Strategies for prevention and treatment
The treatment for muscle atrophy depends on any existing underlying medical condition and the magnitude of muscle loss. Some muscle loss prevention and treatment strategies are as follows:
Resistance training
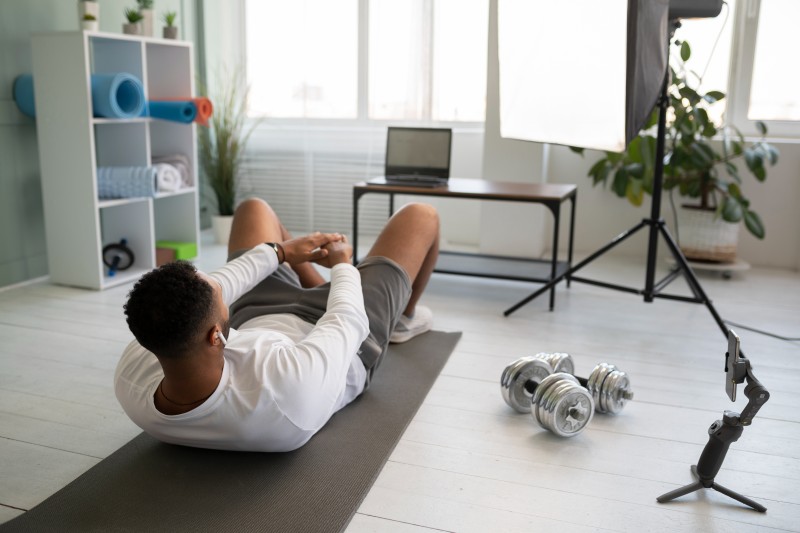

Resistance training is considered the most effective method for preventing and treating muscle loss, particularly as we age. It directly stimulates muscle growth and helps maintain muscle mass by forcing muscles to work against resistance through weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises. Aim for two to three weekly sessions targeting different muscle groups.
Proper nutrition
A balanced diet of fresh fruits and vegetables and regular exercise can reverse the effects of muscle loss. Increase your protein intake through fish, eggs, dairy, beans, nuts, or supplements.
Regular physical activity
Regular physical activity, particularly resistance training, is the most effective strategy for preventing muscle loss. Resistance training directly stimulates muscle growth and helps maintain muscle mass over time. For optimal health benefits, resistance training can be combined with aerobic exercise like walking, swimming, or cycling.
Maintaining a healthy weight
A healthy adult weighs a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9. You can eat nutritious foods, be physically active, and reduce stress to maintain a healthy weight and prevent muscle loss.
Stay strong and healthy
Everyone experiences some muscle loss as they age. But with sarcopenia, this muscle loss happens faster. The good news is – this condition is treatable and reversible. If you have experienced muscle weakness, loss of endurance or any other symptoms of sarcopenia, consult your healthcare provider. They can diagnose the condition and make a treatment plan to reduce the muscle loss and improve your condition to support your overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Muscle loss is the thinning of muscle tissue.
- Aging, inactivity, malnutrition and other factors cause muscle loss.
- Decreased strength, increased fatigue, and changes in gait are its symptoms.
- Incorporate resistance training, proper nutrition, and maintain a healthy weight for prevention.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Keep up to date with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruat ABHI karo.
You may also be interested in the following blogs:
- Can Yoga Build Muscles? Here’s What You Need To Know
- Best Practices For Relieving DOMS (Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness)
Popular Searches
How to lower blood pressure | Fruits good for liver | Unhealthy foods | Ragi Benefits | Basal Metabolic Rate | Acupressure points for High Blood Pressure | Ayurvedic medicine for blood pressure | How to control cholesterol at home | Homeopathy for Asthma | Biological Age | Home remedies for TB | Natural beta blockers | Negative effects of internet | Types of walking | Blood pressure calculator | Blood sugar calculator | BMI Calculator





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000